Как надежный вход через официальный сайт Пин Ап защищает ваши...
Read MoreHave you ever wondered how a gigantic company like Amazon manages to do so many operations from finding products in their warehouse to delivering them all over the world? IIoT, that is, the Industrial Internet of Things plays a big role in making the company’s tasks much easier.
Amazon took the big step of embracing IIoT technology by purchasing an army of Wi-Fi connected Kiva robots way back in 2012. Fast forward seven years later, the Kiva technology has now cut down their operating costs by 20% by taking on the huge task of locating items in the warehouse and providing them to Amazon employees.

What are we trying to achieve with IoT?
Following is an example of a simplified diagnostics system for predictive maintenance of manufacturing equipment. Predictive maintenance is the practice of determining equipment malfunctions before they occur and preventing unnecessary routine maintenance. Achievement of those two goals saves factories millions of dollars in expenses due to considerable reductions of machinery and equipment halts.
System methodology is based on the notation that a malfunction is a consequence of multiple and irregular factors that occur during equipment operation; i.e. a deterioration is a gradual and hopefully measurable process. If the event that led to a malfunction can be measured appropriately, it can be avoided and vice-versa. On the other hand, if such events are not detected, there is no point in doing preventive maintenance.
How would you design an IoT system?
Our simplified example is based on BIG DATA collection and analysis employing signal processing and machine learning techniques. It includes the following modules and layers:
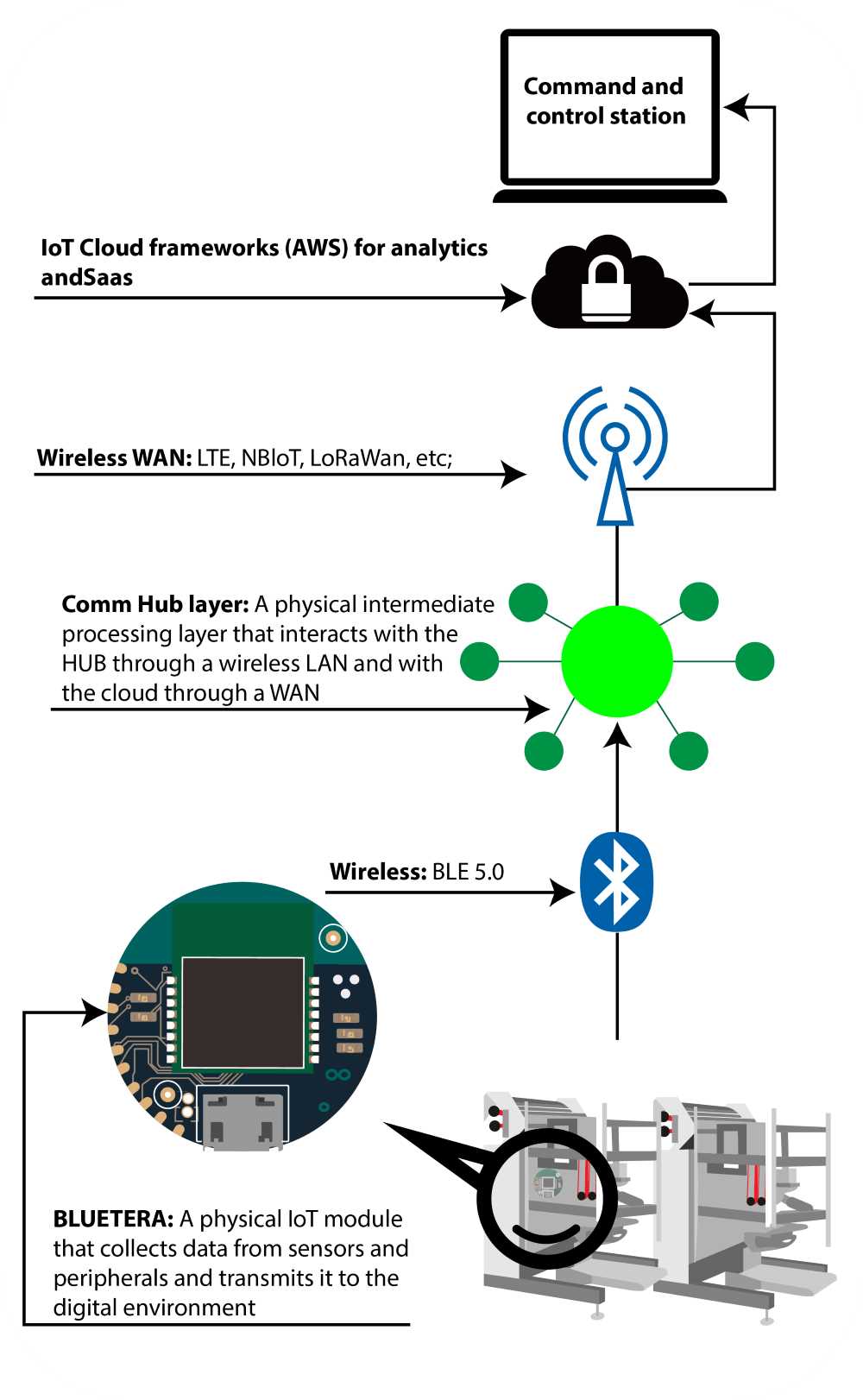
- The sensory layer: Sensors layer: Sensor infrastructure located on the equipment to measure parameters related to the specific machine, e.g. vibration (on motors), temperature, pressure, moisture. New machines may already contain those sensors. However, in many cases, this sensor infrastructure may need to be added or augmented.
- The communication layer: Data aggregated from
the equipment needs to be collected and sent to the analytics platform,
which in many cases is cloud based. Even when the equipment contains local
sensors, it doesn’t have the capability transfer the data remotely.
Communication is divided into three
sub-layers
– The sensors layer which uses wired communication to transfer data from sensors to a local sensors hub.
– Endpoint layer which uses wireless local area network based on BLE 4.x or 5.0 / Thread / Or SubGiga protocols to transfer data between endpoints to nodes.
– And the node layer which uses wireless wide area network based on NBIoT / LoRaWan /LTE to transfer data from nodes to a cloud gateway.
Note that communication system architecture may be different in other systems and use less layers. - Processing layers: Distributed computing techniques are used to process raw data coming from multiple sensors and machines in order to reduce the data rates between layers before final processing at the command & control level.
- Analysis layer: The final layer which is cloud based, processes data coming from multiple sources, as-well-as historical data in order to visualize the operation of the equipment, provide statistics and business intelligence and predict hazardous events. Data from vibration sensors can, for example, pass FFT filters and BE analyzed in the frequency domain. A malfunction of events may be triggered if the frequency differs from predefined thresholds. The analysis layer uses combination of signal processing techniques; Artificial Intelligence; Machine and Deep learning algorithms to make sense of all the BIG data and arrive at logical and beneficial conclusions to predicts events and reduce maintenance. The key factor is to employ the simplest and easies methods that can provide the highest measurable return on investment.
More Posts
1хбет казино скачать: Пошаговая инструкция для новичков
1хбет казино скачать: Пошаговая инструкция для новичков В этой статье...
Read MoreПинко казино отзывы: экспертный взгляд на платформу
Пинко казино отзывы: экспертный взгляд на платформу Пинко казино —...
Read More